Genetic Symphonies
the building hox of life
Animals, humans, and every living creature has DNA. We all even share much of the same DNA!
You can think of DNA as the recipe book for life. DNA contains information called genes, which contain instructions for making proteins.
Both vertebrates (humans and animals with a spine) and invertebrates (animals without spines) share a unique set of genes, known as Hox genes. There are 13 groups of Hox genes that help guide development as they signal what gets built and when. Unlike other genes, Hox genes must be activated in a certain order, from top to bottom - starting with Hox1 and ending with Hox13 - for development to occur.
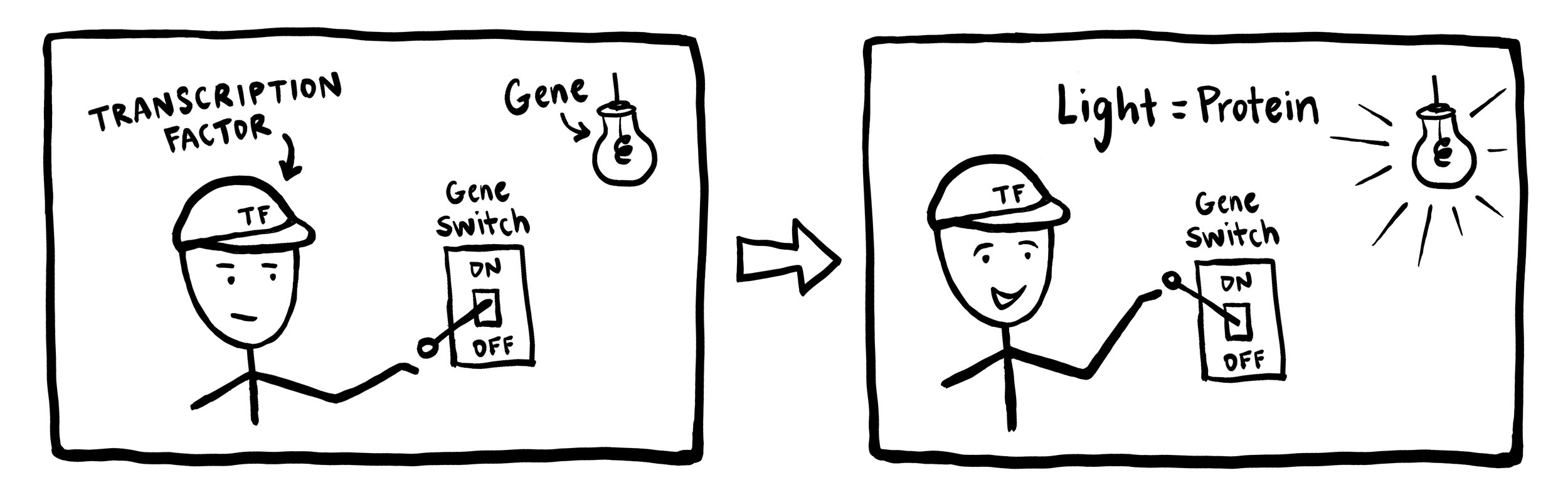
When Hox genes turn on, they make proteins. Proteins have all sorts of roles in the body, from acting like support beams (like bones and muscles) to being connectors for different body parts. Hox genes make special proteins called transcription factors that control when other proteins are made. Transcription factors do this by directly interacting with DNA to switch other genes “on” or “off.”
In this exhibit, you can press buttons to switch on the 13 Hox genes, represented here as blocks. Hox genes must be activated in a specific order - Press the buttons in the correct order to orchestrate your own developmental symphony!
Can YOU figure out the correct order for the 13 Hox genes?
-
Hox genes are activated from top (Hox1) to bottom (Hox13), or head to tail.
Music note stems and boxes are color coordinated.
Each button activates a unique musical sequence and illuminates one box.
There is a different combination of instruments for every button. The number of instruments you hear represents the Hox gene number.
Did you enjoy this installation? Click below to see the correct sequence and please help fill out our survey so we can learn how to better connect science with the public!
If you are having trouble accessing this page, download the pdf version of this experience.
Art Design & Fabrication: Sharon Tang; Music & Electronics: Katharine Hubert. Copyright 2023, Kohler Fellows @WID.
Many thanks to the Kohler Foundation, the Wisconsin Institute for Discovery, the University of Wisconsin-Madison Makerspace, and the McBurney Disability Resource Center, with special acknowledgements to Matthew Mabee, John Lombardo, Yash Wani, Tim Steis, and Ryan D. Ward for fabrication guidance and Deneen Wellik for scientific consultation.
If you have website accessibility questions or suggestions, please email sharon.tang@wisc.edu.